Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Diagnostic performance of the 2022 KLCA-NCC criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma on magnetic resonance imaging with extracellular contrast and hepatobiliary agents: comparison with the 2018 KLCA-NCC criteria
- Ja Kyung Yoon, Sunyoung Lee, Jeong Ah Hwang, Ji Eun Lee, Seung-seob Kim, Myeong-Jin Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):157-165. Published online February 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.07

- 1,508 Views
- 89 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
This study aimed to determine the diagnostic performance of 2022 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center (KLCA-NCC) imaging criteria compared with the 2018 KLCA-NCC for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in high-risk patients using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
This retrospective study included 415 treatment-naïve patients (152 patients who underwent extracellular contrast agent [ECA]-MRI and 263 who underwent hepatobiliary agent [HBA]-MRI; 535 lesions, including 412 HCCs) with a high risk of HCC who underwent contrast-enhanced MRI. Two readers evaluated all lesions according to the 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC imaging diagnostic criteria, and the per-lesion diagnostic performances were compared.
Results
In “definite” HCC category of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC, HBA-MRI showed a significantly higher sensitivity for the diagnosis of HCC than ECA-MRI (77.0% vs. 64.3%, P=0.006) without a significant difference in specificity (94.7% vs. 95.7%, P=0.801). On ECAMRI, “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of the 2022 KLCA-NCC had significantly higher sensitivity than those of the 2018 KLCA-NCC (85.3% vs. 78.3%, P=0.002) with identical specificity (93.6%). On HBA-MRI, the sensitivity and specificity of “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC were not significantly different (83.3% vs. 83.6%, P>0.999 and 92.1% vs. 90.8%, P>0.999, respectively).
Conclusions
In “definite” HCC category of both 2018 and 2022 KLCA-NCC, HBA-MRI provides better sensitivity than ECA-MRI without compromising specificity. On ECA-MRI, “definite” or “probable” HCC categories of the 2022 KLCA-NCC may improve sensitivity in the diagnosis of HCC compared with the 2018 KLCA-NCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the updated KLCA-NCC criteria for diagnosis of “probable HCC” in liver MRI: comparisons between KLCA v2022 and v2018
Jeong Hee Yoon
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 124. CrossRef
- Impact of the updated KLCA-NCC criteria for diagnosis of “probable HCC” in liver MRI: comparisons between KLCA v2022 and v2018

Case Reports
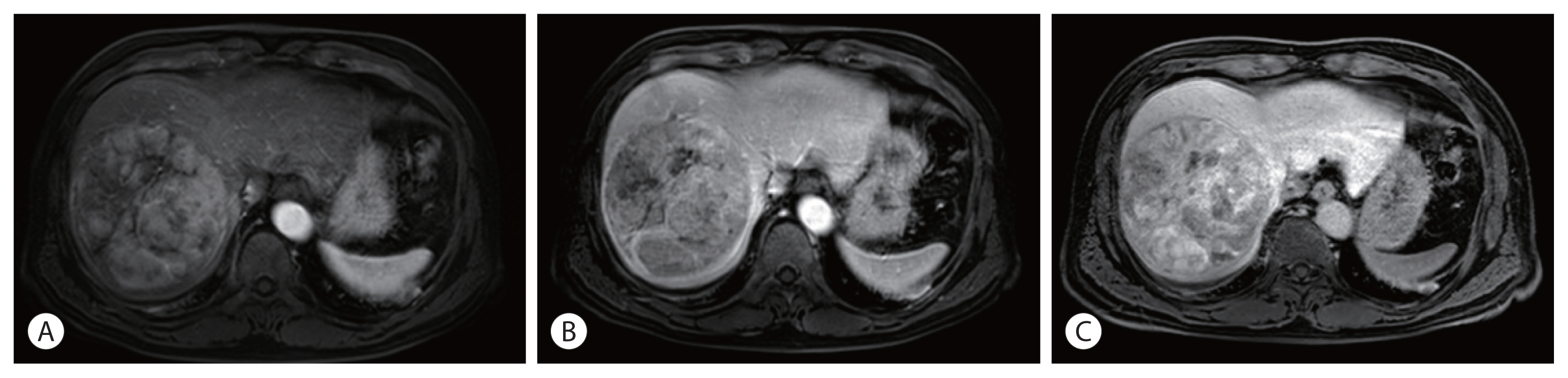
- Ruptured Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cured by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Ji Eun Lee, Joong-Won Park, In Joon Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, Seoung Hoon Kim, Hyun Beom Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):154-159. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.154
- 2,902 Views
- 62 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Spontaneous tumor rupture is a serious but rare complication of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has a low survival rate. Here, we report a case of massive HCC that ruptured and was treated successfully with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A 55-year-old man with abdominal pain was diagnosed with a 12-cm-wide ruptured HCC at segment 8. The overall liver function was scored as Child–Pugh A, but the single nodule tumor had ruptured; therefore, TACE treatment was initiated. After the first TACE treatment, residual tumors were found; thus, secondary TACE was performed 5 months later. No new lesions or extrahepatic metastases were found 16 months after the first TACE treatment, so hepatic resection was performed for curative treatment. The postoperative pathology results did not reveal any cancer cells; hence, TACE alone resulted in a cure. We report this case because the cure has been maintained for more than 3 years after resection.

- A Case of Mechanical Obstruction after Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Ji Eun Lee, Jae Young Jang, Soung Won Jeong, Sae Hwan Lee, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim, Young Deok Cho, Hong Soo Kim, Boo Sung Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):195-198. Published online September 30, 2011
- 569 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) inducing of coagulation necrosis by using thermal energy via electrodes placed within the tissue effectively controls hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). RFA has been commonly applied as an alternative curative therapy to surgical resection for small HCC due to effective local tumor control. Although the technique is considered relatively safe, several major complications requiring hospitalization for treatment have been reported such as vascular thrombosis, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, skin burn, hematoma, liver abscess and colon perforation. Most complications occur due to thermal injuries to adjacent structures by RFA. The risk of bowel perforation has been observed only when the target lesion is adjacent to a gastrointestinal lumen, but, mechanical obstruction is extremely rare. Therefore, we report a case of mechanical obstruction after transaction of ileum secondary to RFA of HCC.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter